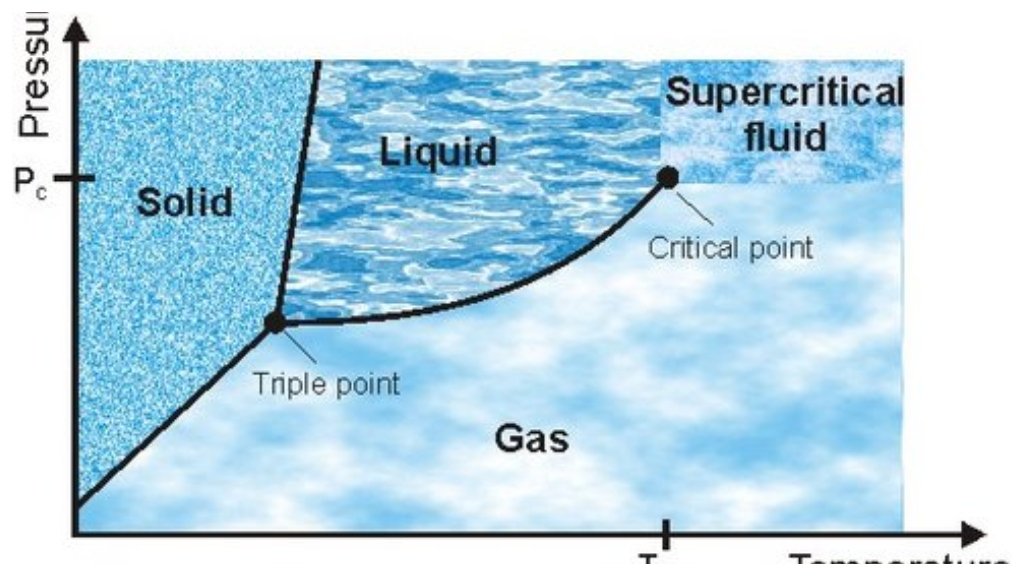
Supercritical fluids are materials with temperature and pressure above their critical point. In this state, they also have unique properties, as they combine properties of liquids and gases. This post examines these intriguing fluids in terms of their nature and applications.
What Are Supercritical Fluids?
Supercritical fluids are substances that exist beyond their critical point, where the distinction between liquid and gas phases disappears. In this state, supercritical fluid exhibits both high density (akin to a liquid) and low viscosity (similar to a gas). They can diffuse through solids, just as gases do, while dissolving materials, just as liquids do. Because some substances, such as carbon dioxide and water, have relatively low critical temperatures and pressures, they are commonly used in supercritical form.
Properties of Supercritical Fluids
These physical properties enable supercritical fluids to possess unique and valuable capabilities across a range of applications. They are as dense as liquids and can therefore dissolve things exceptionally well. Their viscosity is closer to that of gases, allowing them to penetrate porous materials easily. This is what grants supercritical fluids their unique and high solvent power.
These characteristics are greatly affected by temperature and pressure. This enables the tuning of material solubility with supercritical fluids by adjusting these variables. They are well-suited to particular processes, such as extraction and purification, due to their versatility.
Applications in Extraction and Purification
The most frequent application of supercritical fluids is for extraction and purification processes. For example, supercritical carbon dioxide is commonly used for extracting essential oils, flavors, and fragrances. It selectively dissolves compounds so you can extract high-purity extracts without the use of toxic solvents.
It retains the flavor and aroma of the drinks compared to traditional methods. Moreover, supercritical extraction is also employed by the pharmaceutical industry to isolate compounds, ensuring that the final product is free from contamination.
Role in Environmental Technology
Much attention has been given to environmental technology associated with supercritical fluids and the process of supercritical fluid chromatography. They provide an alternative to toxic solvents used in industrial processes, minimizing an ecological footprint. Supercritical water oxidation is the most widely used technology for treating hazardous waste. Repurposing this organic mass leaves a minimal footprint by decomposing it into harmless end-products, which is more sustainable than burning it into ashes.
Another environmental application involves the use of the supercritical fluid approach for polymer recycling. These separation technologies facilitate the selective and efficient dissolution of polymers, enabling easy recovery and encouraging sustainable waste management through effective recycling processes.
Innovations in Material Science
Supercritical fluids are employed in material science to develop new materials exhibiting improved functional performances. They enable the creation of aerogels, low-density and highly porous materials that are excellent thermal insulators. Supercritical drying prevents the collapse of the gel, resulting in a stable material with outstanding insulating properties.
Moreover, supercritical fluids are used in the synthesis of nanoparticles. Knowing how to dissolve and transport materials at the nanoscale enables control over these factors as well as particle size and distribution.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, there are challenges in utilizing such supercritical fluids. The need for specialized tools that can withstand high pressures, high temperatures, and stringent cleanliness levels can come with a price tag. Additionally, the behavior of materials in supercritical states is quite complex, and the purification of supercritical components is a precise and somewhat challenging task. Supercritical fluid processes are still being developed to achieve cost reductions and expand their applications.
Conclusion
Due to their unique combination of properties, supercritical fluids are widely utilized across various industries. They are essential and play a relevant role, from extraction and purification to environmental technology and material science. Although hurdles remain, current research and advances will further expand the potential uses of these technologies. Leveraging these fluids has the potential to provide more efficient and sustainable solutions in a range of industries. Click here for more information.